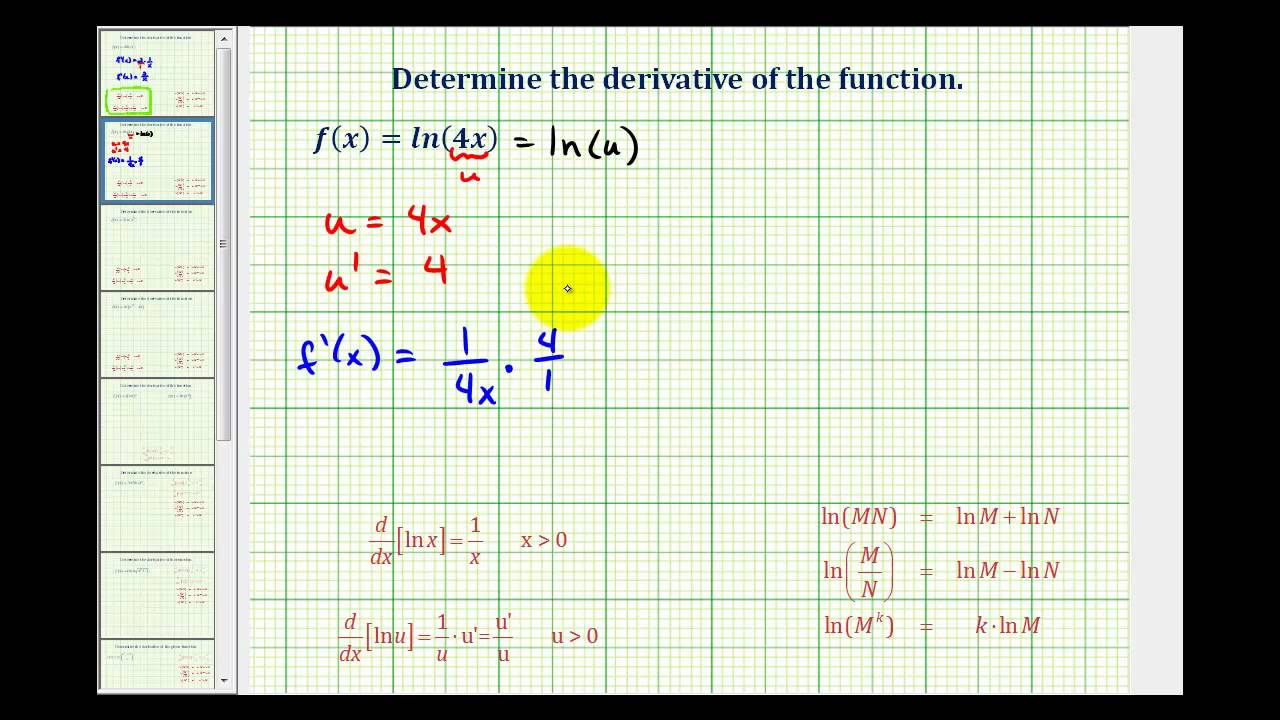
We know how to differentiate ln(x) (the answer is 1/x) This means the chain rule will allow us to perform the differentiation of the function ln(4x) To perform the differentiation, the chain rule says we must differentiate the expression as if it were just in terms of x as long as we then multiply that result by the derivative of what the expression was actually in terms of (in this and so y = lnu ⇒ dy du = 1 u substitute these values into (A) changing u back to terms of x ⇒ dy dx = 1 u (2x) = 2x 1 x2 Answer linkE y = x Then base e logarithm of x is ln(x) = log e (x) = y The e constant or Euler's number is e ≈ Ln as inverse function of exponential function The natural logarithm function ln(x) is the inverse function of the exponential function e x For x>0, f (f 1 (x)) = e ln(x) = x Or f 1 (f (x)) = ln(e x) = x Natural

Derivative Calculator Wolfram Alpha
Partial derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)^(1/2)
Partial derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)^(1/2)-Derivative calculator This calculator evaluates derivatives using analytical differentiation It will also find local minimum and maximum, of the given function The calculator will try to simplify result as much as possible Derivative of y = ln u (where u is a function of x) Unfortunately, we can only use the logarithm laws to help us in a limited number of logarithm differentiation question types Most often, we need to find the derivative of a logarithm of some function of xFor example, we may need to find the derivative of y = 2 ln (3x 2 − 1) We need the following formula to solve such problems



Partial Derivatives
Weekly Subscription $249 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $799 USD per month until cancelled Holidays Promotion Annual Subscription $1999 USD for 12 months (40% off) Then, $3499 USD per year until cancelledWell, we know how to take the derivative of u of x and v of x, u prime of x here, is going to be equal to, well remember, square root of x is just the same thing as x to 1/2 power, so we can use the power rule, bring the 1/2 out from so it becomes 1/2 x to the, and then take off one out of that exponent, so that's 1/2 minus one is negative 1/2 power Homework Statement Find the derivative of 1 / ln x Homework Equations N/A The Attempt at a Solution y = 1/lnx First Attempt y' = 1/x/(lnx)^2
1) For absolute value of (x) < 1, the derivative of y= ln SQRT (1x^2) is I have 1/ SQRT(1x^2) for the regualkr derivative but I am not sure how "for absolute value of (x) < 1" would change the answer if it does 2) The tangent line to the graph e^2x at the point (1,e) intersects both coordinate axesDerivative of x^2y^2 \square!Find the derivative of the function \(y = \ln(x^2)\) Solution Before applying any calculus rules, first expand the expression using the laws of logarithms Here, we can use rule (1) This step is all algebra;
Answer (1 of 10) It is also possible to find this derivative using the definition of the derivative, or \begin{align} f'(x) = \displaystyle \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{fAn online derivative calculator that differentiates a given function with respect to a given variable by using analytical differentiation Write sin1 x as asin(x) 2 Write ln x as ln(x) 5 Sample Inputs for Practice Eg1 Write (10x2)(x 2) as 10*x2x^2 2Derivative of 1/ (x^21) \square!



How To Solve For The Derivative Of Y Ln X 1 X 1 2 2x 2 Quora



Calculus Derivative Of The Natural Log Ln Video Lessons Examples Solutions
Let The derivative of is Then, apply the chain rule Multiply by Apply the quotient rule, which is and To find Differentiate term by term The derivative of the constant is zero The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function This is a small part of a bigger problem, but the part I am having trouble with is finding the derivative of lnsqrt(x^2y^2) I'm sure it is something simple and I remember learning it in Calc I or II but I forgot Please help remind me! y = ln (tanh (x/2)) Find the derivative of the function y=ln (tanh (x/2)) The derivative formula of natural logarithm is d/dx ln (u) = 1/u* (du)/dx Applying this formula, the derivative of the function will be y' = d/dx ln (tanh (x/2)) y' = 1/ (tanh (x/2)) * d/dx tanh (x/2) To take the derivative of hyperbolic tangent, apply the formula



Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt X 2 1 Vs Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt X 2 1 Youtube



Y Ln X Sqrt X 2 A 2 Find Dy Dx Youtube
Since the interchange just changes the sign of the right hand side, it follows that w yy = −w xxLeaving us with the derivative of ln x, which is 1/x The constant 2 comes out of the differentiation The 2 multiplied by 1/x is written as 2/x Step 3 Simplify Thus, the derivative of ln x2 is 2/x Note this result agrees with the plots of tangent lines for both positive and negative xStep 3 Simplify The 2 multiplied by 1/ x is written as 2/ x Thus, the derivative of ln x2 is 2/ x Note this result agrees with the plots of tangent lines for both positive and negative x For



5 5 The Differentiation Of Logarithmic Functions Let Y Ln X X 0




Question Video Deriving The Inverse Function Of An Exponential Function Nagwa
I have worked through this problem, but am not sure of my answer I am supposed to find the derivative of $y=\ln(x\sqrt{x^2a^2})$, $a$ being a constant We know how to differentiate ln(x) (the answer is 1/x) This means the chain rule will allow us to perform the differentiation of the function ln(2x) To perform the differentiation, the chain rule says we must differentiate the expression as if it were just in terms of x as long as we then multiply that result by the derivative of what the expression was actually in terms of (in thisDerivative of ln (x^2y) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process
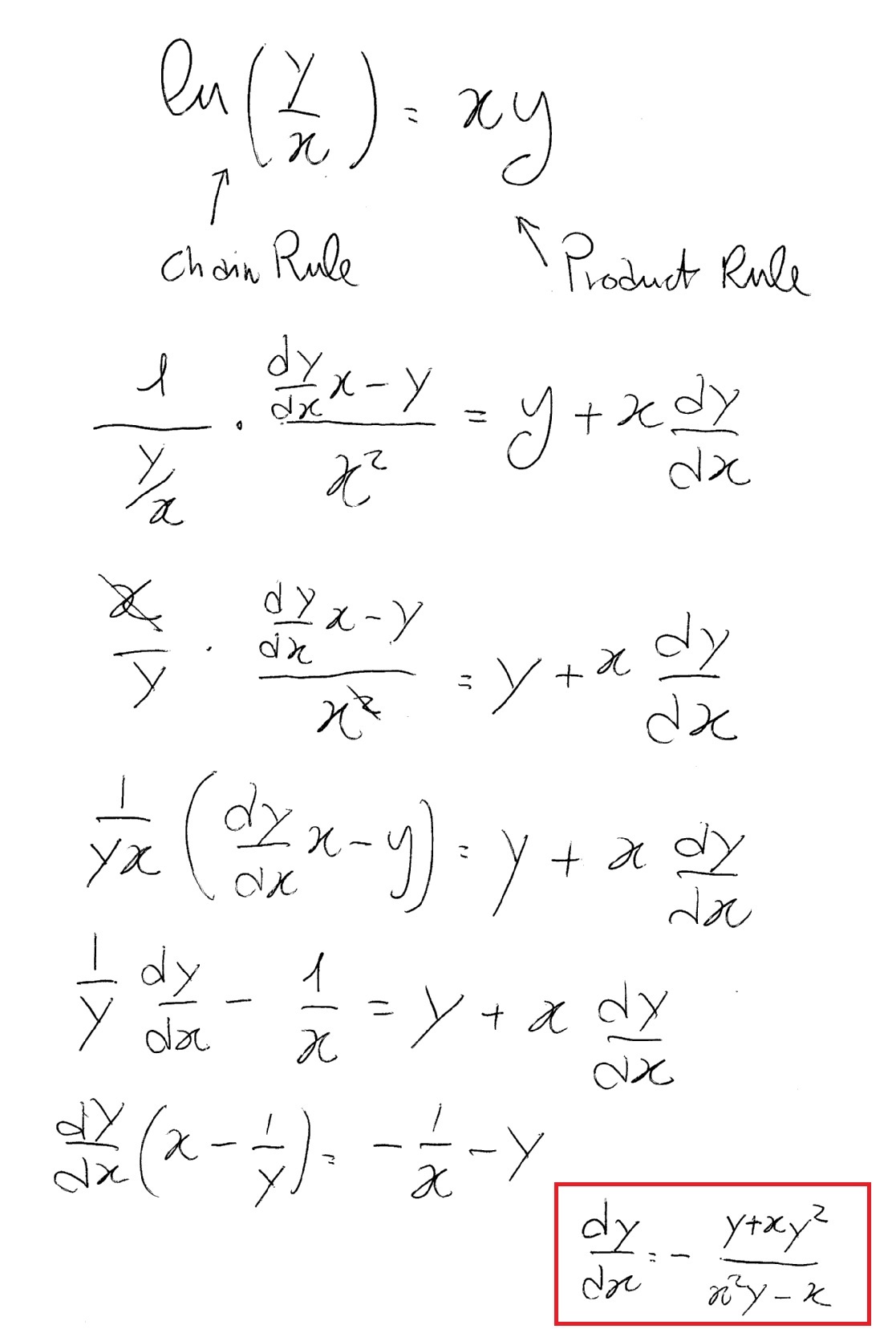



How Do You Differentiate Ln Y X Xy Socratic



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
This is called logarithmic differentiation It's easiest to see how this works in an example Example 1 Differentiate the function y = x5 (1−10x)√x2 2 y = x 5 ( 1 − 10 x) x 2 2 Show Solution Differentiating this function could be done with a product rule and a quotient rule However, that would be a fairly messy processGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!X2 y2 (x2 y2)2 w = ln(x 2 y 2 ) remains the same, while w xx gets turned into w yy ;




Derivative Calculator Wolfram Alpha
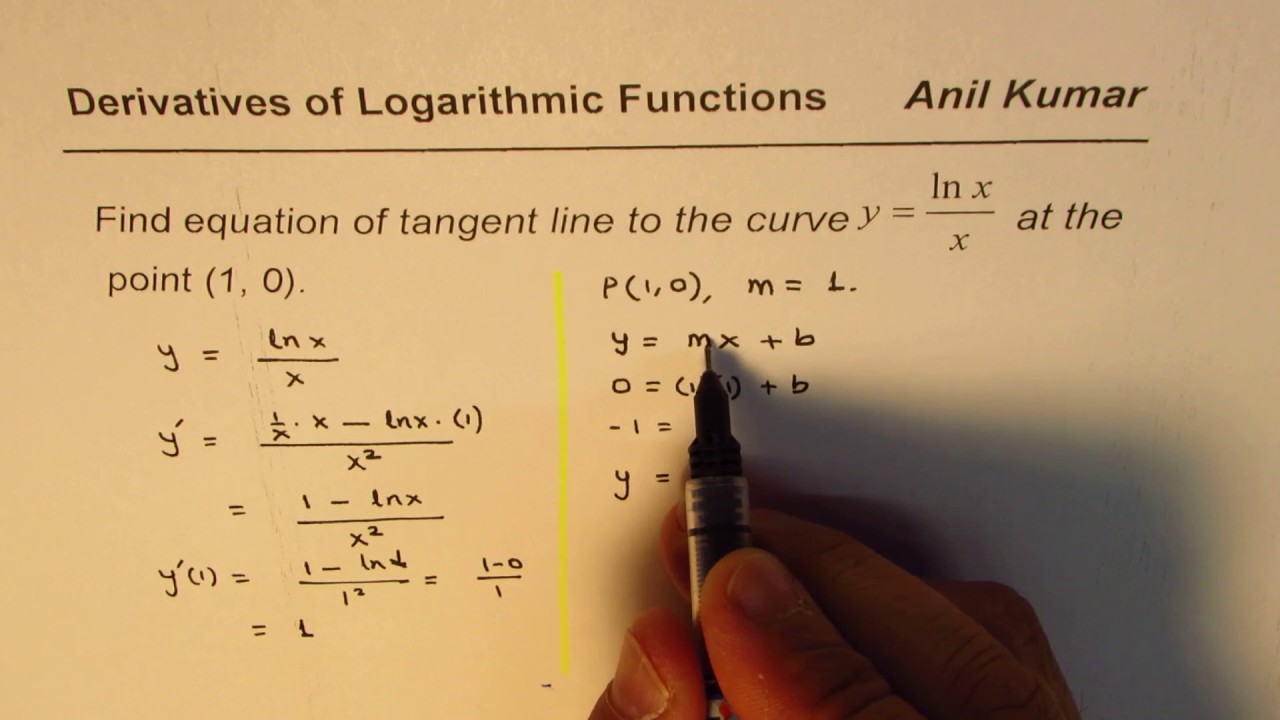



Implicit Derivation Of Logarithmic Function Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube
As we can see, taking the derivative of ln requires differentiating the function inside of the natural log and dividing that by the function inside of the natural log Here are two example problems showing this process in use to take the derivative of ln Problem 1 Solve d ⁄Derivative of ln (ln (2^x)) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processWorked problem in calculus The derivative of f(x) = ln(ln(x^2 1)) is calculated using the chain rule twice




Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
In this lesson I will show you how to differentiate (ln x)^2 using the Chain RuleThis video illustrates the tangent line to the 3D surface to illustrate the meaning of the value of a directional derivativewebsite http//mathispower4ucomThe derivative of y in terms of x is denoted by `(dy)/(dx)` or `y'` For the given problem `y = 1/2(1/2ln((x1)/(x1)) arctan(x))` , we may apply the basic differentiation property `d/(dx) c
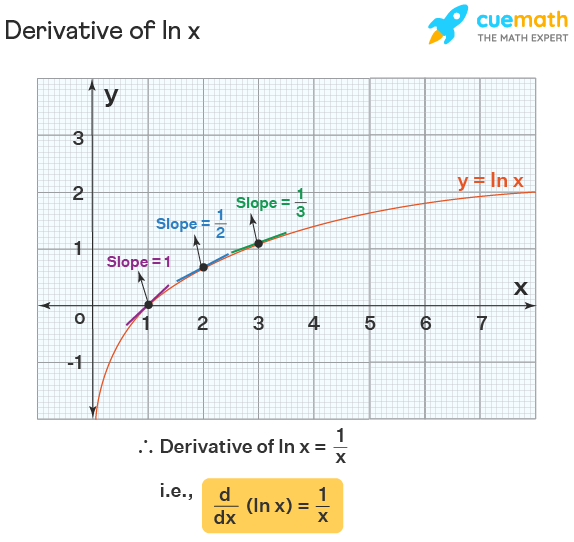



Derivative Of Ln X Formula Proof Examples



Solved Find The First Derivative Of Y Y Ln X Squareroot Chegg Com
Solved Find the derivative of the following functions y=(x^{2}1)\ln x Plainmath recommends Ask your own question for free Get a detailed answer even on the hardest topicsAnswer (1 of 6) Y = (2X 1)^2 X^3 => Y' = 2(2X 1)(2) 3X^2 => Y' = 8 X 4 3X^2 Y'' = 8 6X I am new to partial derivatives and they seem pretty easy, but I am having trouble with this one ∂ ∂ x ln ( x 2 y 2) now if this was just d d x ln ( x 2) we would get 2 x x 2 So I feel we would get ∂ ∂ x ln



Find The Derivative Of The Following 1 Y Exln X Gauthmath



Larson Calculus 13 3 28 First Partial Derivatives Of G X Y Ln Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Youtube
Derivative of ln(1/(1x^2)) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem no, he didn't forget the square root he changed \(\displaystyle \L \ln{\sqrt{1x^2}}\) to \(\displaystyle \L \frac{1}{2} \ln(1x^2)\) using the power law for logsNo calculus is done until after we expand the expression \(y = \ln(x^2) = 2\ln(x)\) Now, take the derivative This is the calculus step



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
2x d (y 2)×dy = 3 dy dx 2x 2y dy = 3 dx dy = 3 2x dx 2y Example Differentiate a x with respect to x You might be tempted to write xa x1 as the answer This is wrong That would be the answer if we were differentiating with respect to a not x Put y = a xGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us! How to calculate the derivative of ln^2(x) Note that in this post we will be looking at differentiating ln 2 (x) which is not the same as differentiating ln(x 2) or ln(2x)Here are our posts dealing with how to differentiate ln(x 2) and how to differentiate ln(2x) There are two methods that can be used for calculating the derivative of ln^2(x)



Derivative 1 2 1 2 Ln X 1 X 1 Arctanx Mathskey Com



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic
Derivative of Ln(x2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem The derivative of ln(x) with respect to x is (1/x) The derivative of ln(s) with respect to s is (1/s) In a similar way, the derivative of ln(2x 2) with respect to 2x 2 is (1/2x 2) We will use this fact as part of the chain rule to find the derivative of ln(2x 2) with respect to x How to find the derivative of ln(2x 2) using the Chain Rule
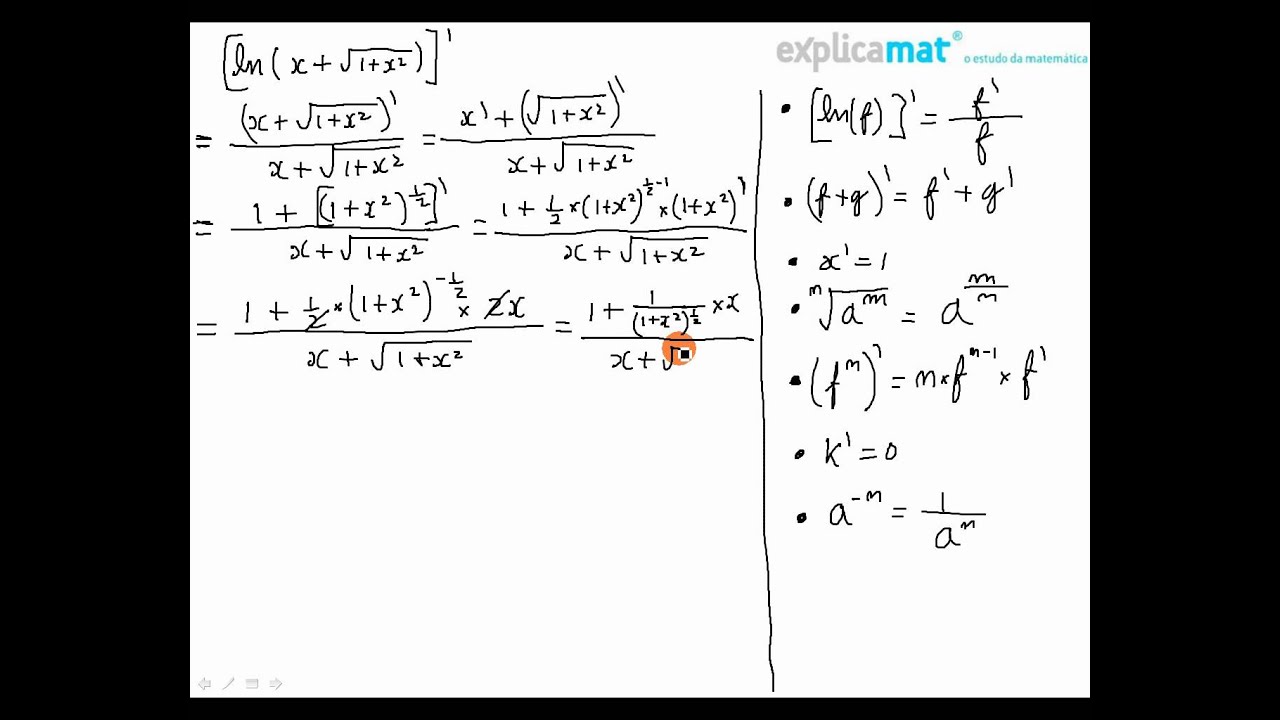



Derivada Logaritmo Ln X Sqrt 1 X 2 Youtube




Ppt Section 3 5 Find The Derivative Of G X X 2 Ln X You Will Need To Use The Product Rule Powerpoint Presentation Id



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Practice 4 With Solutions Engr 301 Engineering Management Studocu
.gif)



Calculus Differentials And Integrals




How Do You Find The Derivatives Of Z Ln Y 4 1 2 Y 1 3 Homeworklib
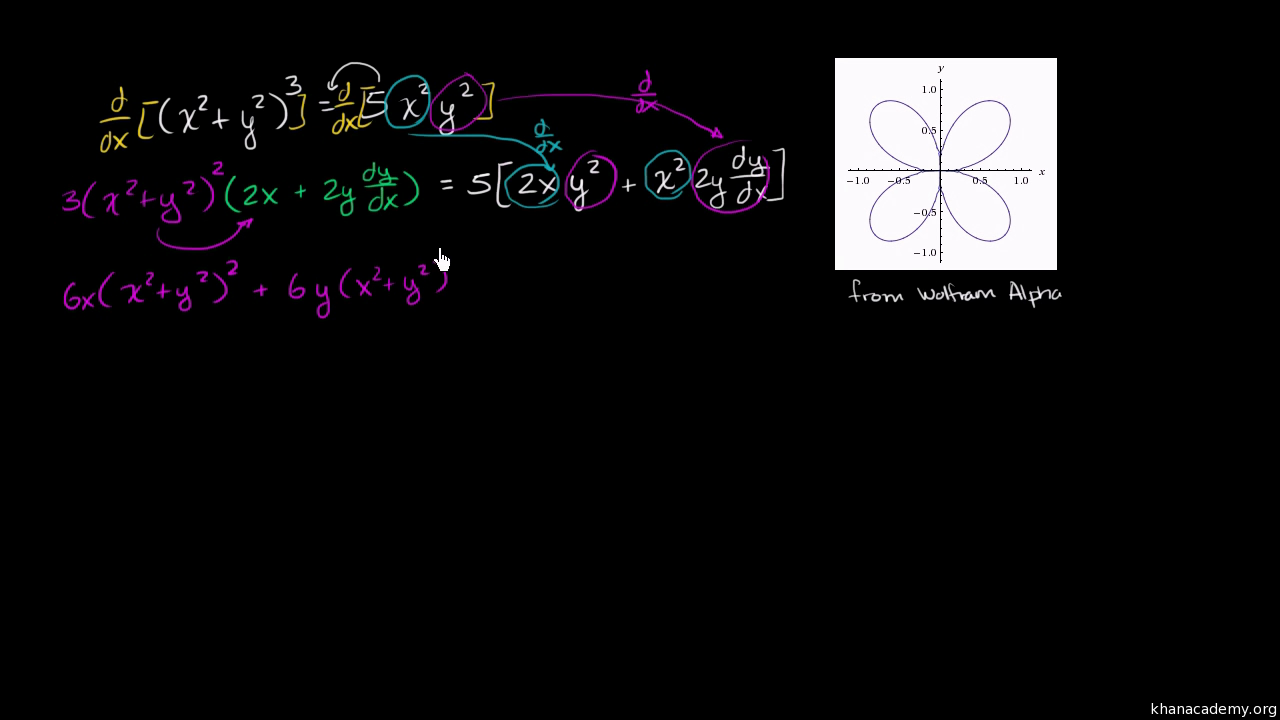



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
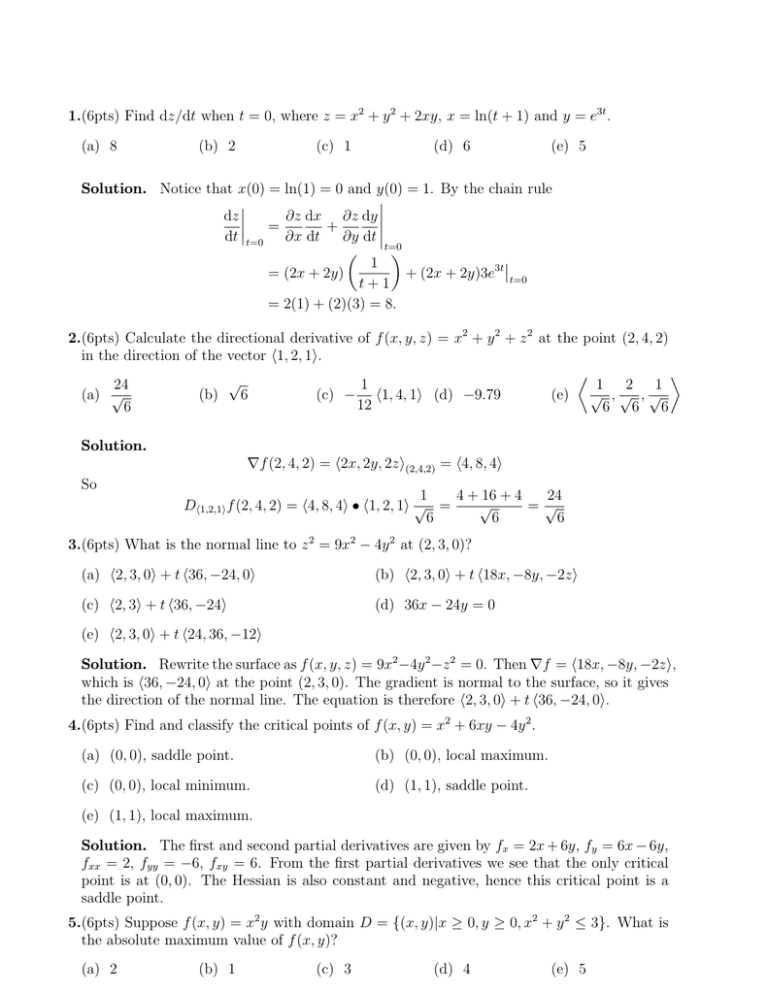



1 6pts Find Dz Dt When T 0 Where Z X 2 Y2 2xy X Ln T 1
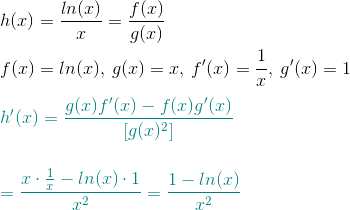



Finding The Derivative Of Ln X X How To Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
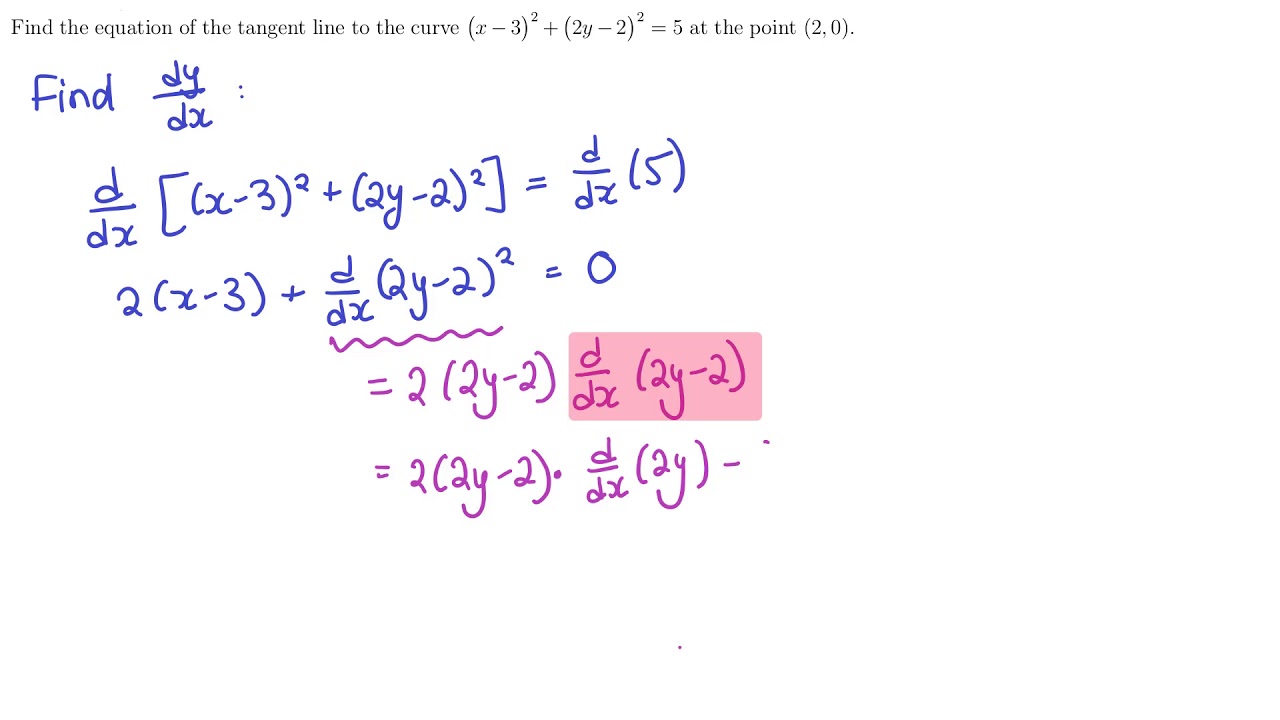



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
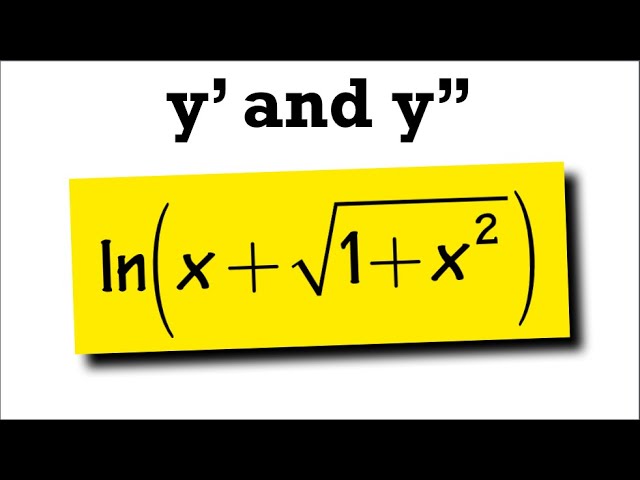



Second Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt 1 X 2 Youtube




Max And Min X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
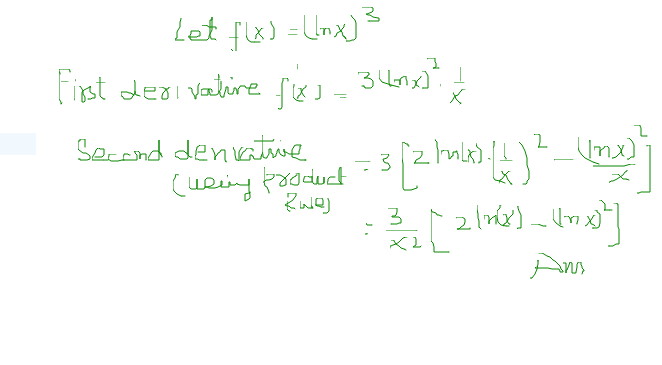



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Lnx 3 Socratic
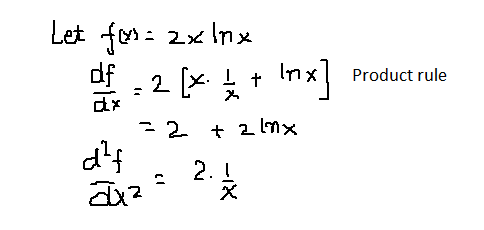



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of 2x Ln X Socratic
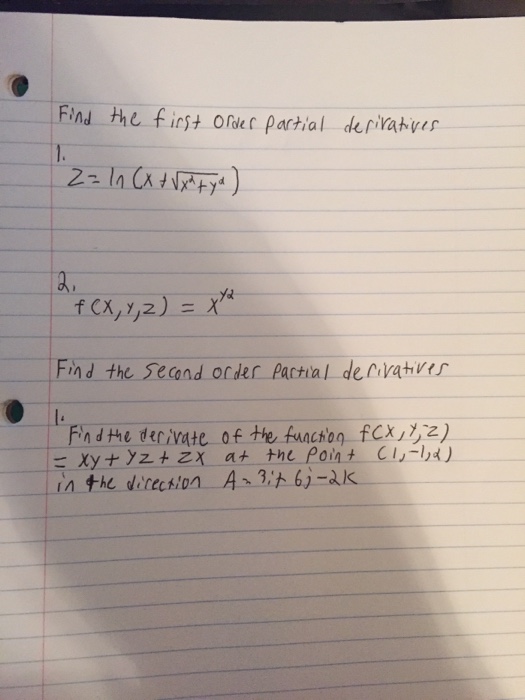



Solved Find The First Order Partial Derivatives Z Ln X Chegg Com




Derivative Rules



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1



1




How To Prove That F X Ln X 2 1 Is Not Uniform Continuous Mathematics Stack Exchange



Partial Derivatives



How To Find Dy Dx Of The Function Y X 1 X 2 X 1 2 Quora
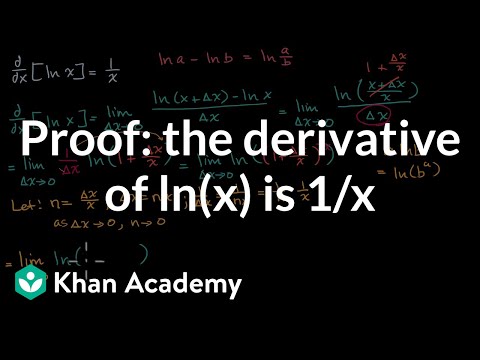



Proof The Derivative Of Ln X Is 1 X Video Khan Academy
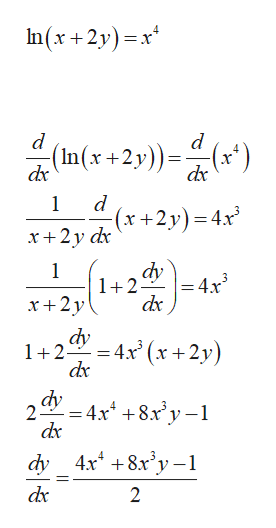



Answered Suppose Ln X 2y X4 Use Implicit Bartleby




Solved Help Please For 1 2 6 Find The First Order Partial Chegg Com



Ualberta Ca
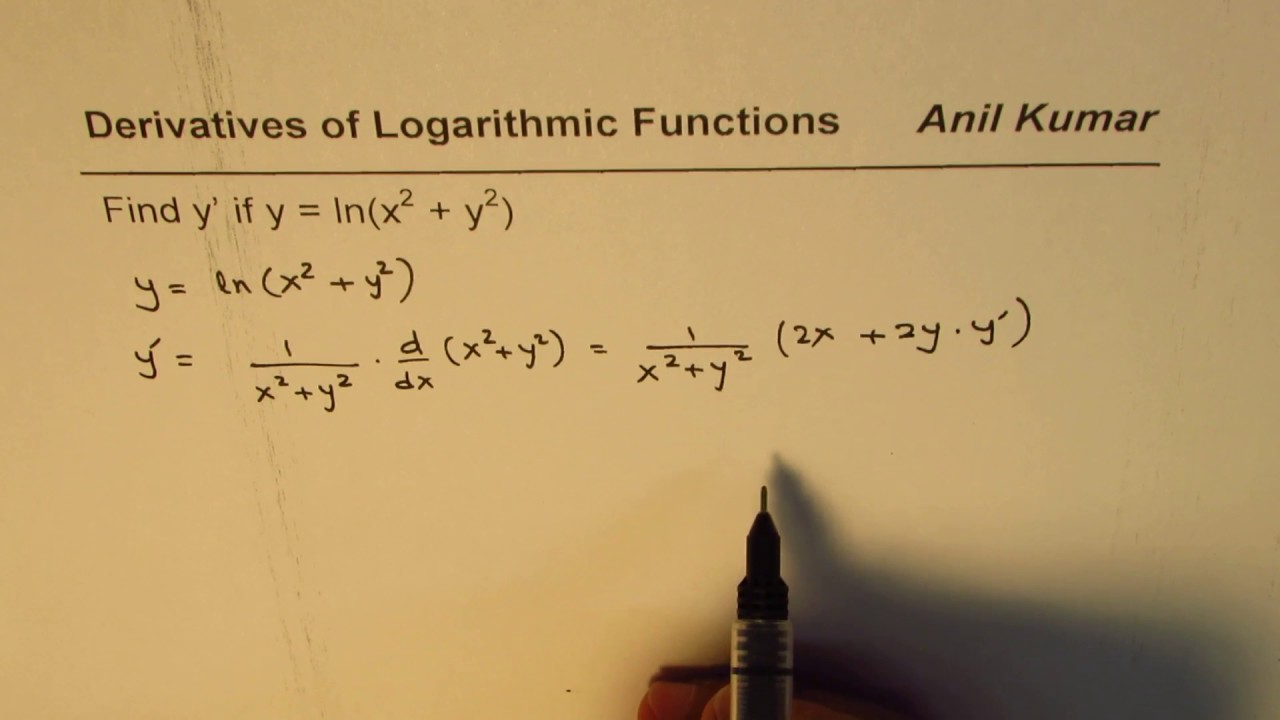



Implicit Derivation Of Logarithmic Function Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube




Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More



If Y X 2 2 1 2 X X 2 1 Ln X X 2 1 Prove That 2y Xy Lny Where Denotes The Derivative Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
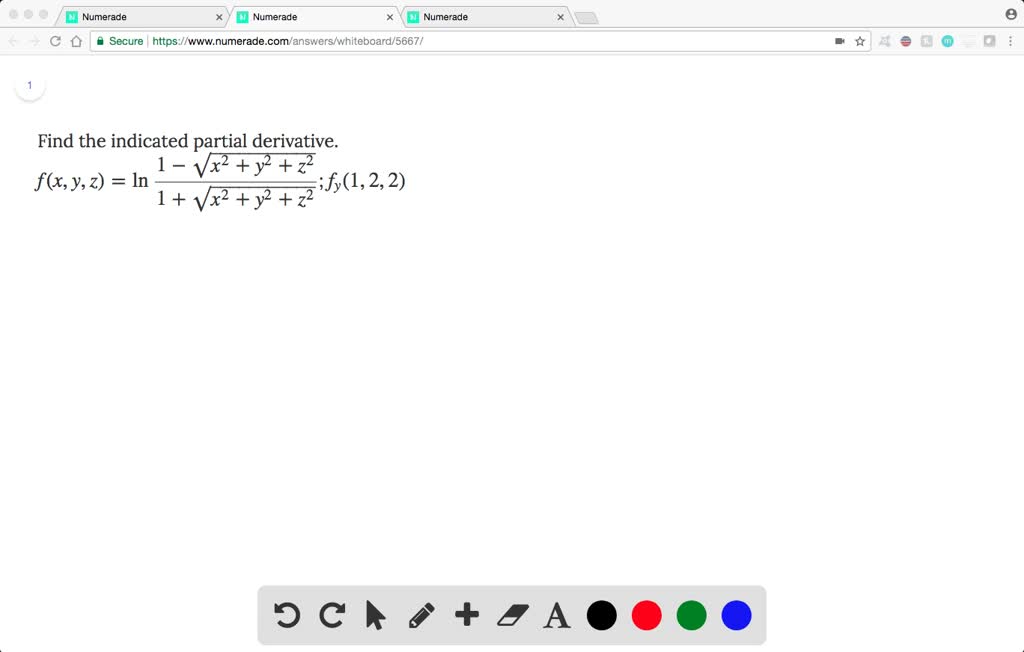



Solved Find The Indicated Partial Derivative F X Y Z Ln Dfrac 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 F Y 1 2 2



How To Differentiate Ln X 2 Using The Chain Rule Youtube




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download




Find Y For Ln X Y Arctan Xy Mathematics Stack Exchange




Math 148 Exam Iii Practice Problems




Solved Find The Derivative Of Y With Respect To X Y Chegg Com




How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Ln X X 2 1 1 2 Homeworklib
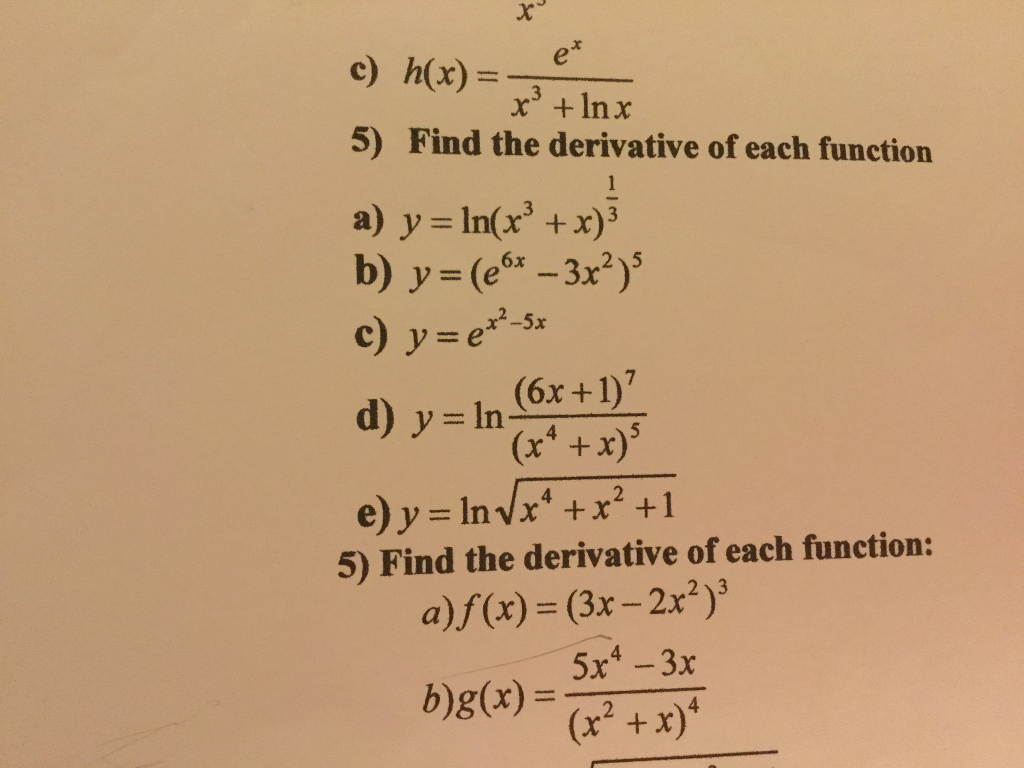



Solved Find The Derivative Of Each Function Y Ln X 3 Chegg Com



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More



14 3 Partial Differentiation




Natural Logarithm Wikipedia




Practice Problems 10 And 11




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download




First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Youtube
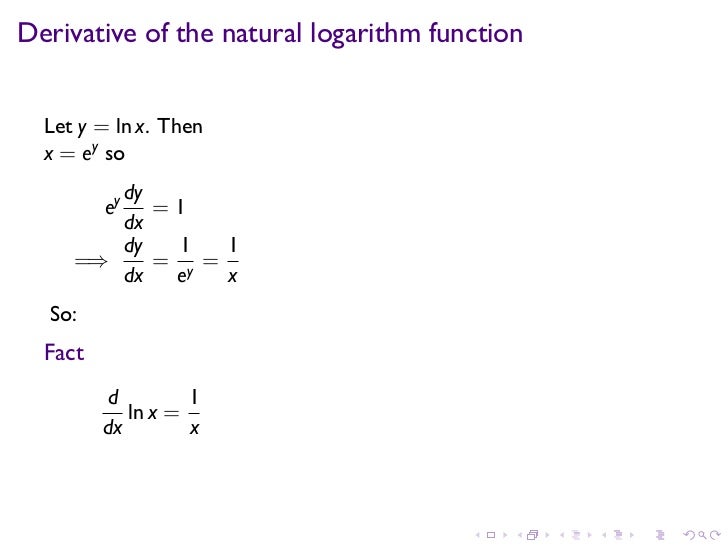



Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions
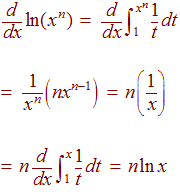



Logs And Derivatives
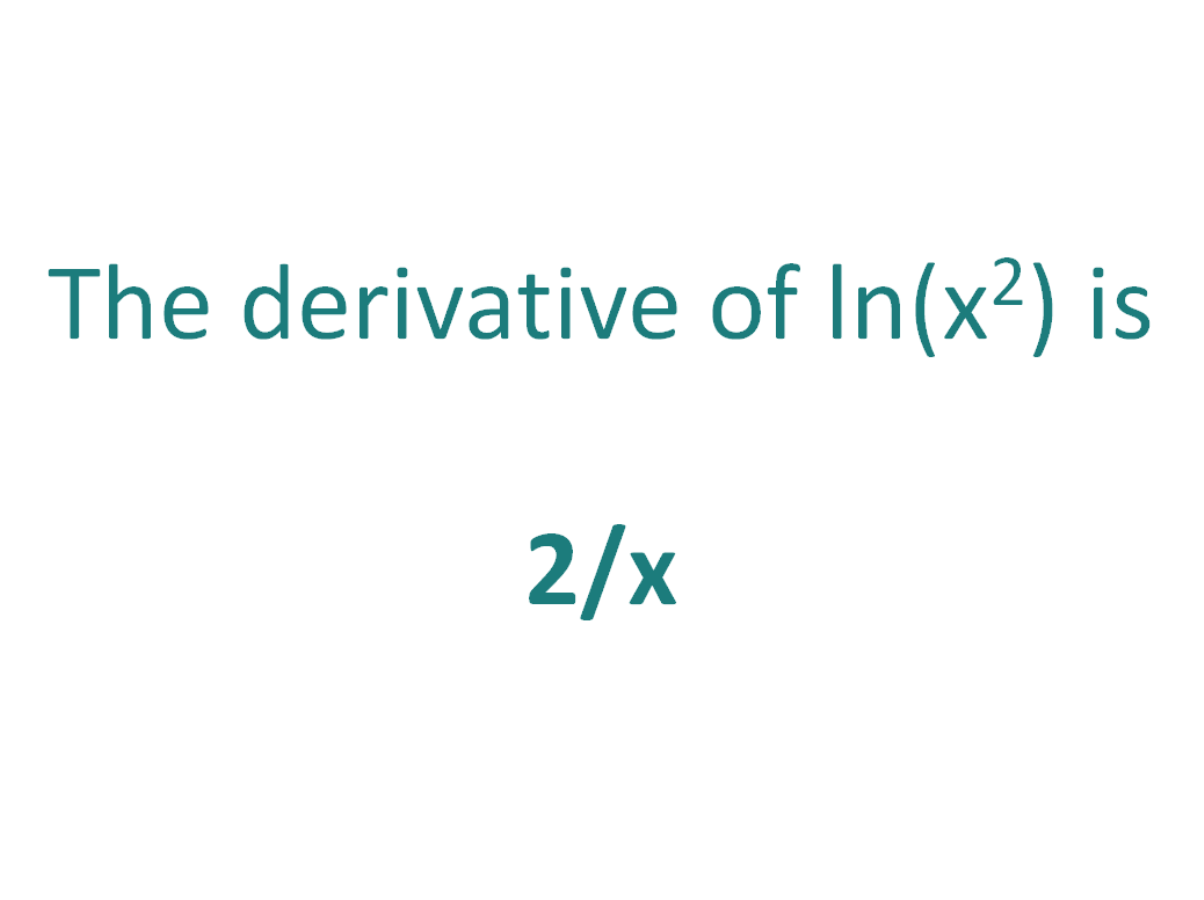



The Derivative Of Lnx 2 Derivativeit
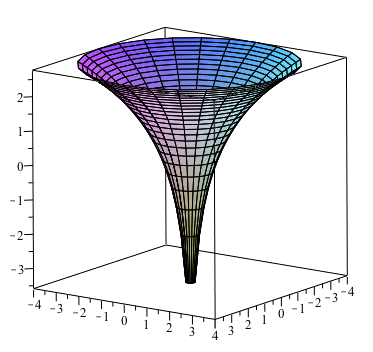



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic



7 1 The Natural Logarithm Function



Implicit Differentiation




Solved Let Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Determine The Derivative Y At Chegg Com



Www3 Nd Edu



What Is The Integrating Factor Of Math X Ln X Dy Dx Y 2 Ln X Math Quora




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More
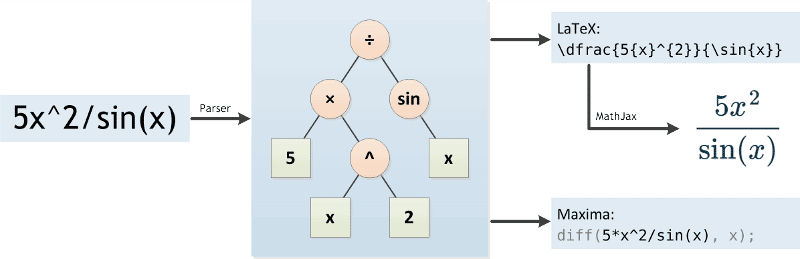



Derivative Calculator With Steps
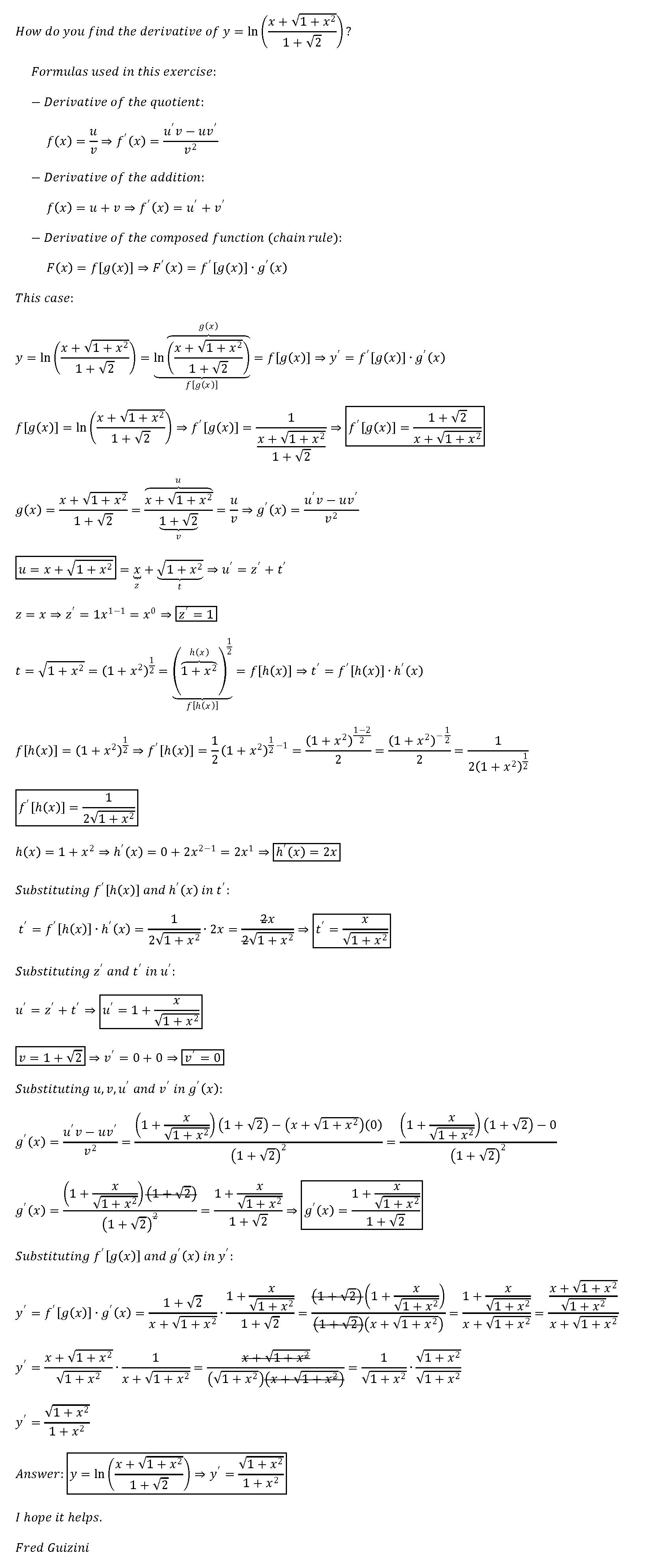



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y Ln X Sqrt 1 X 2 1 Sqrt2 Socratic




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps
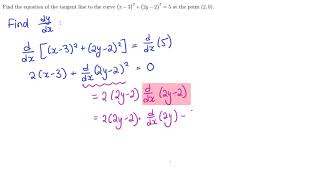



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Answered 54 Y Ln X Cos Cos X 3d Bartleby
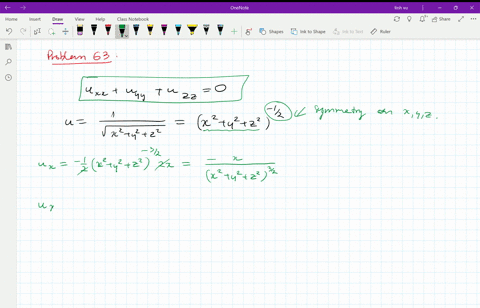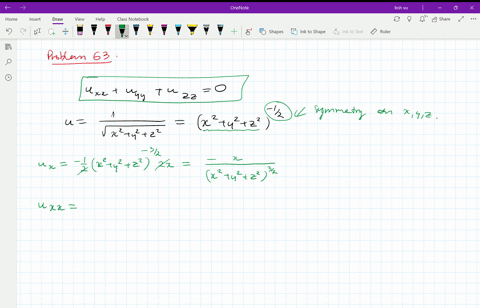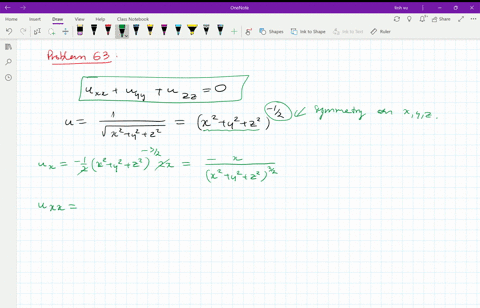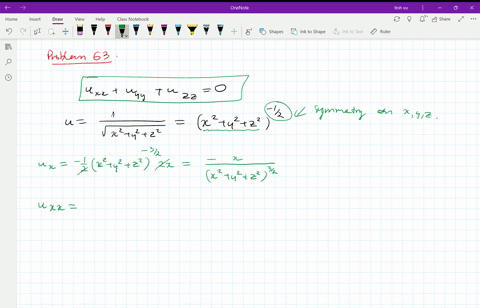



Solved Verify That The Function U 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Is A Solution Of The Three Dimensional Laplace Equation U X X U Y Y U Z Z 0




Derivatives Days Ppt Download
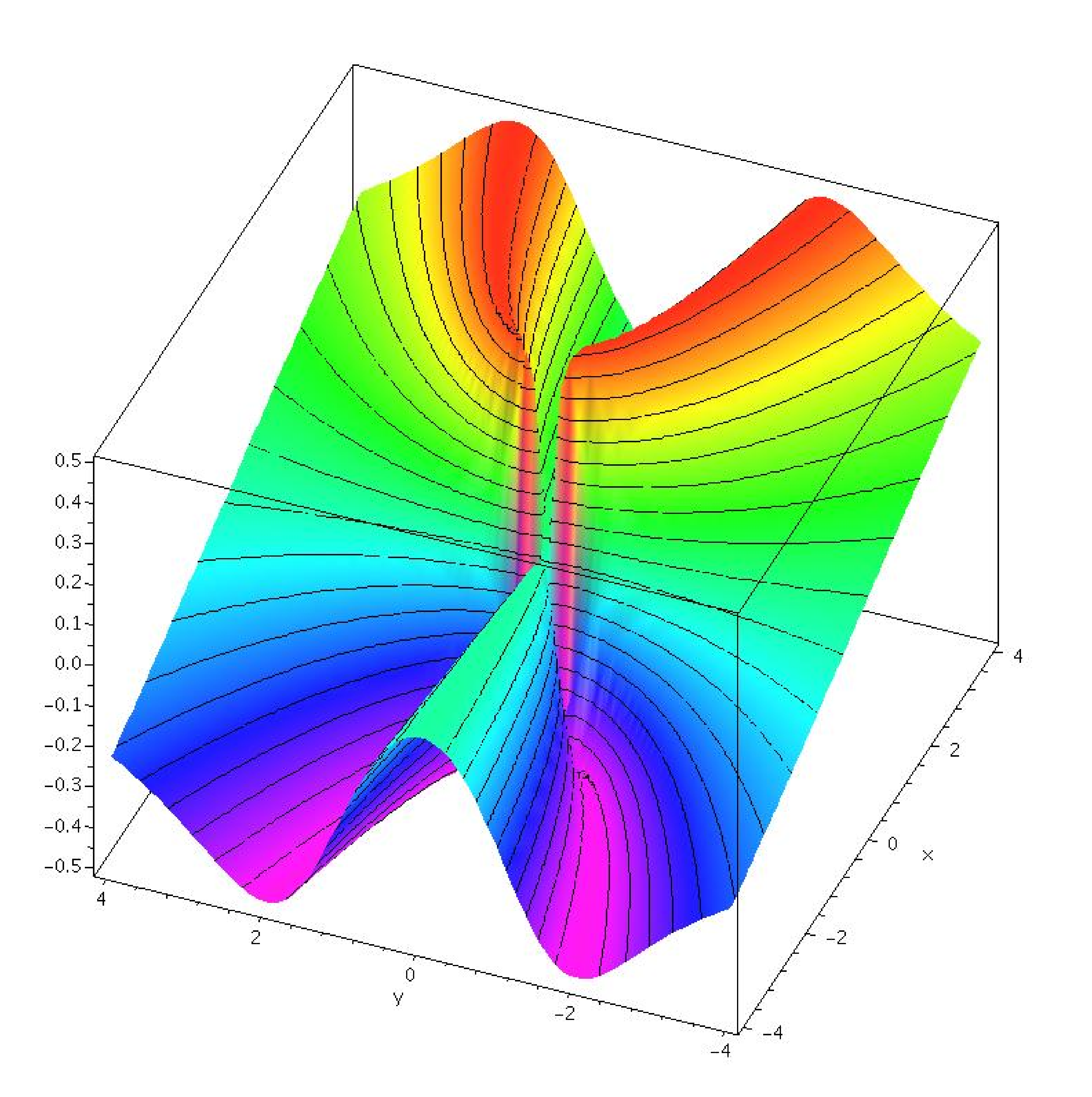



14 2 Limits And Continuity
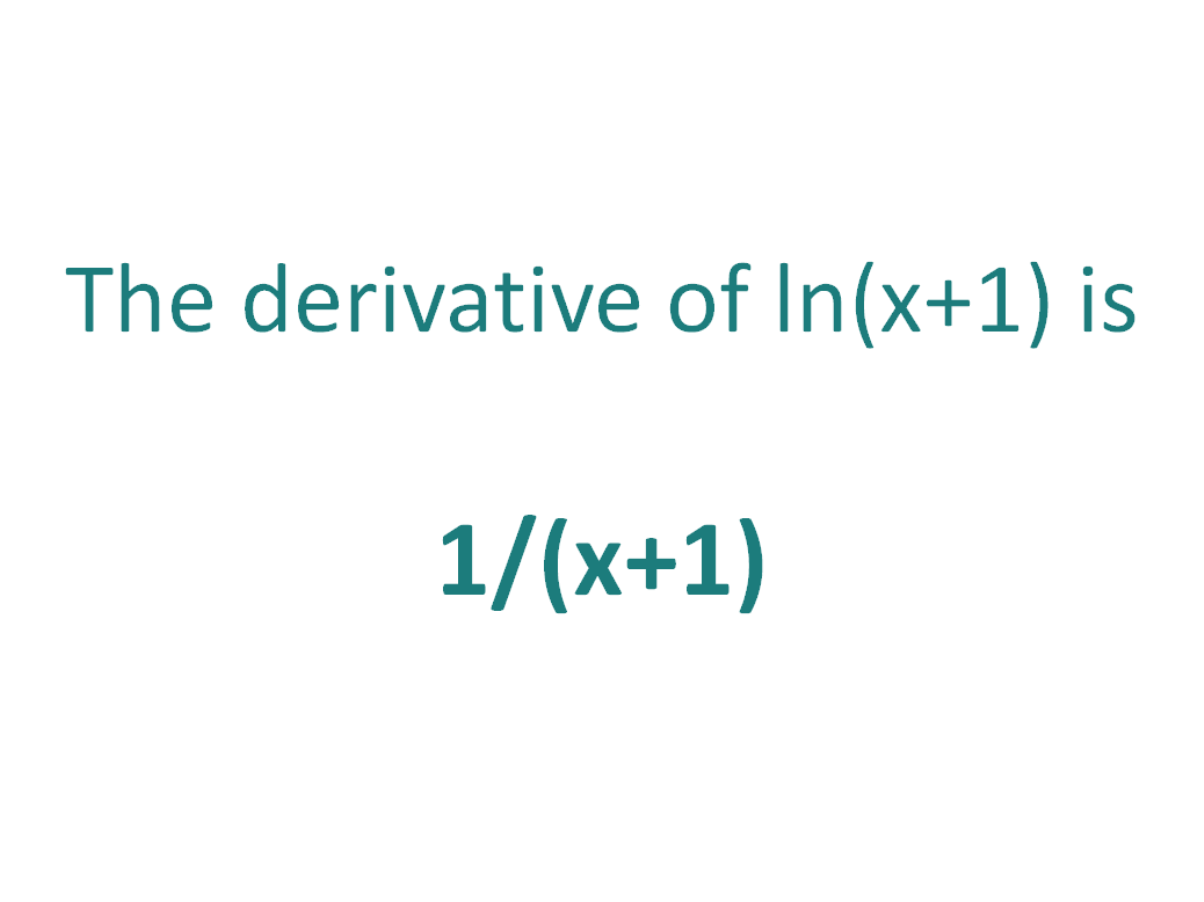



The Derivative Of Ln X 1 Derivativeit



Webassign Net



3



3



What Is The Differentiation Of Y Ln X With Respect To X Where Represents Modulus Function Quora




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
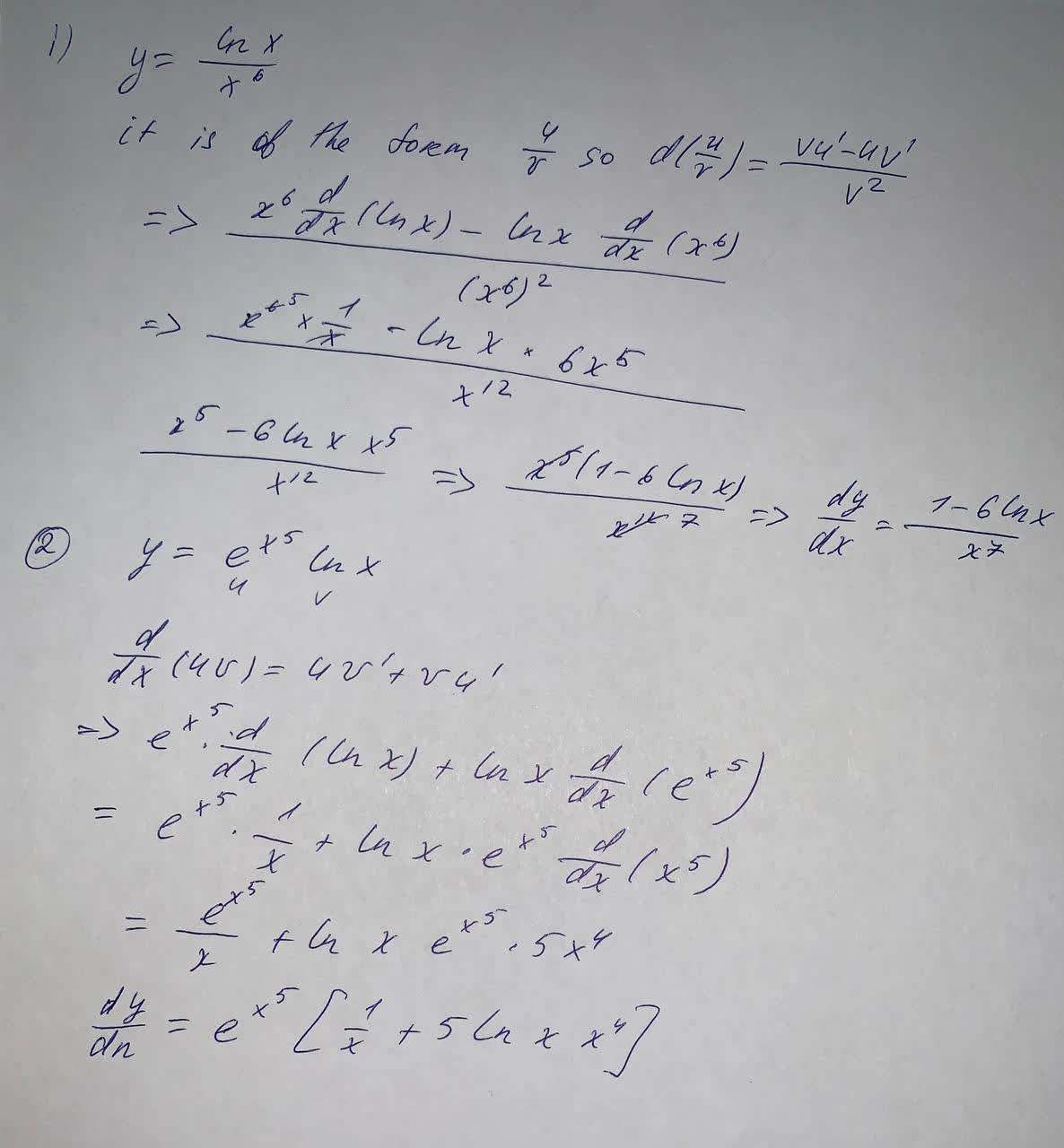



Find The Derivative Y Frac Ln X X 6 Y E X 5 Ln X Find The Indicated Derivative Of Plainmath




3 9 Derivatives Of Ln General Exponential Log Functions And Logarithmic Differentiation Mathematics Libretexts
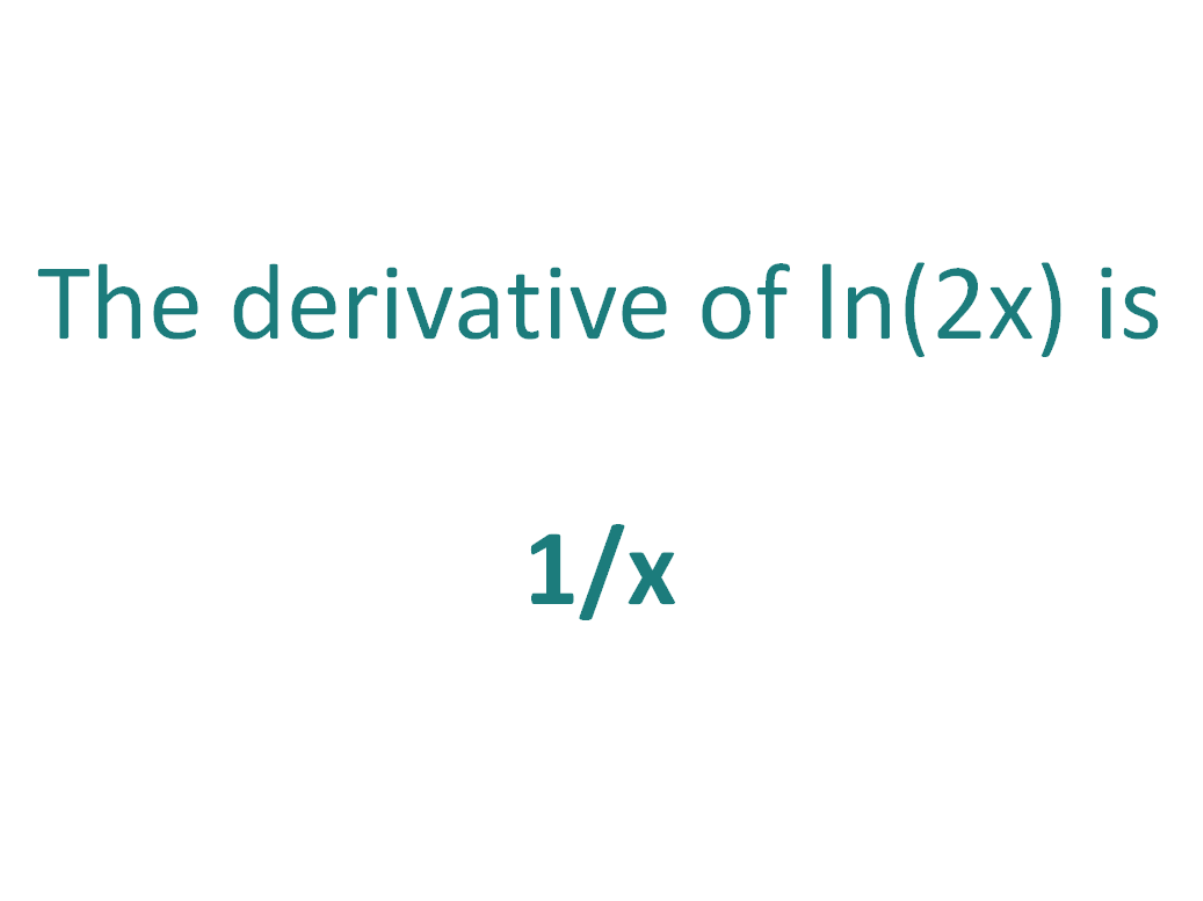



The Derivative Of Ln 2x Derivativeit




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download
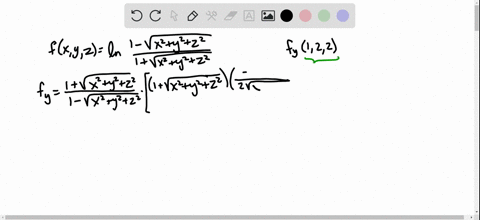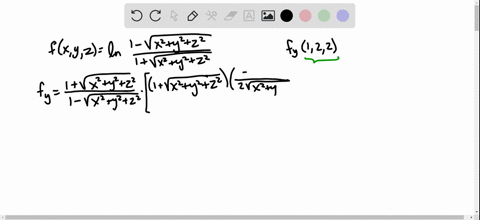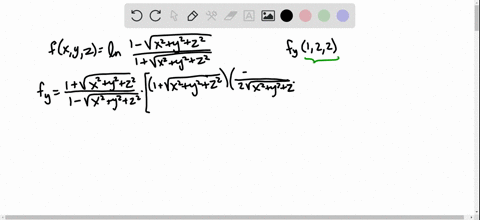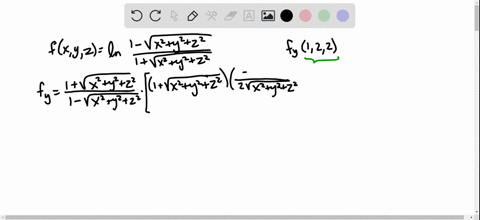



Solved Find The Indicated Partial Derivative F X Y Z Ln Dfrac 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 F Y 1 2 2




Worked Example Derivative Of Ln X Using The Chain Rule Video Khan Academy



Amherst Edu
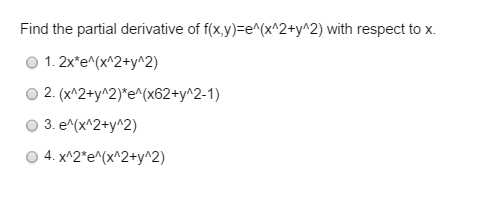



Solved Find The Partial Derivative Of F X Y E X2 Y2 With Chegg Com




Derivative Of Ln X Formula Proof Examples
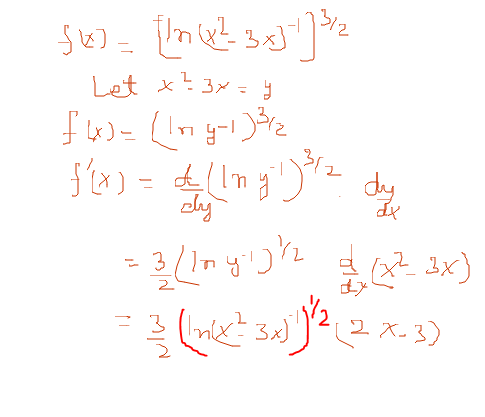



How Do You Differentiate F X Ln X 2 3x 1 3 2 Using The Chain Rule Socratic




If Log X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 Yx Then Prove That Dydx X Yx Y
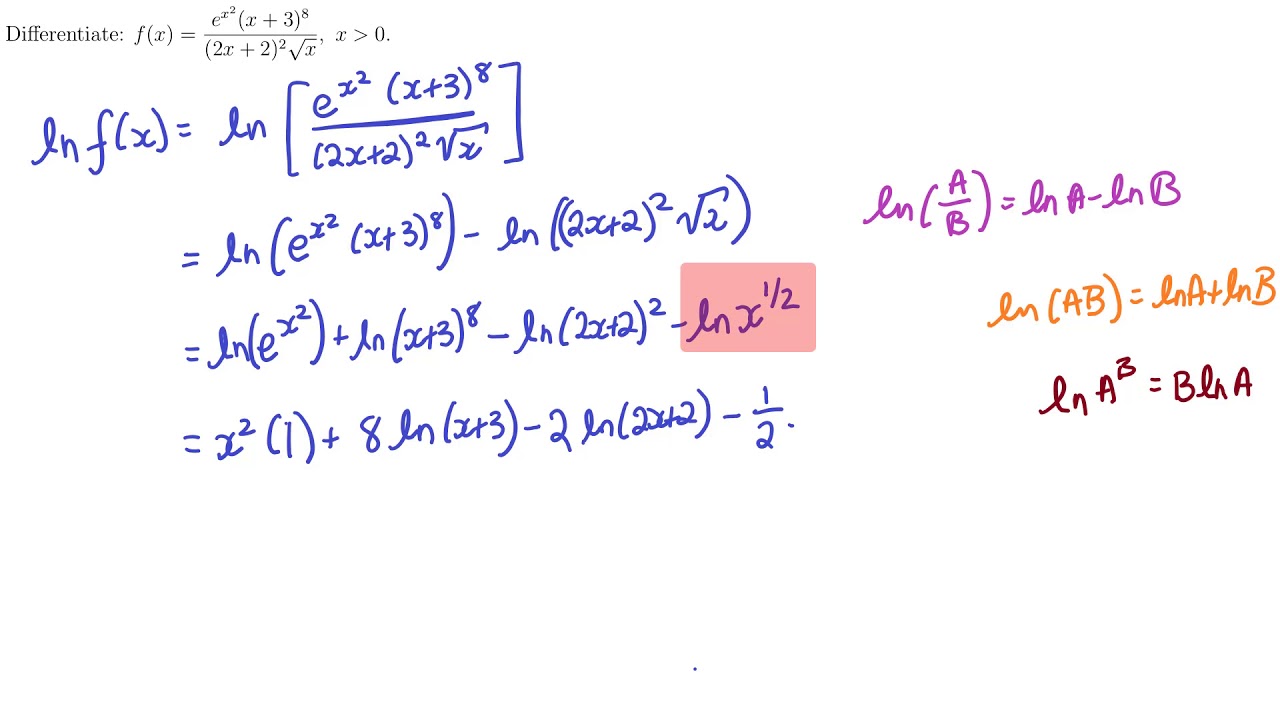



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿